 Class Definition
Class Definition
A Class describes an Object COBOL Class object and its instance objects. It contains nested programs for class methods and instance methods.
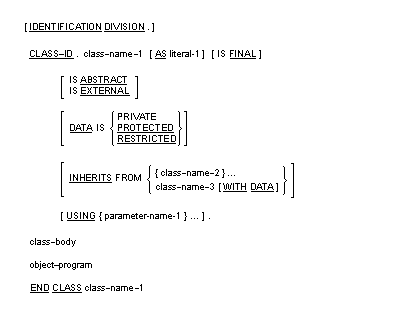
General Format
Syntax Rules
- The words PROTECTED and RESTRICTED are equivalent.
- If the EXTERNAL clause is specified, neither the DATA nor the INHERITS clause may be specified.
- If the ABSTRACT clause is specified, the FINAL clause must not be specified.
- If the WITH DATA phrase is specified in the INHERITS clause, the DATA IS PRIVATE clause must not be specified explicitly or implicitly in the source code for class-name-2.
- Class-name-2 must not be the same as class-name-1.
- Class-name-2 must not inherit from class-name-1 directly or indirectly.
- Class-name-1 in the END CLASS header must be identical to the class-name-1 specified in the preceding Class-ID paragraph.
General Rules
- Class-name-1 identifies the class being declared.
- The ABSTRACT clause indicates that class-name-1 is an abstract class. You cannot create an instance of an abstract class.
- The EXTERNAL phrase indicates that class-name-1 is an external class. No code is produced.
- The RESTRICTED phrase enables subclasses to directly access data inherited from class-name-1.
- The PRIVATE phrase prevents subclasses from directly accessing data inherited from class-name-1.
- The INHERITS phrase specifies that class-name-2 is a parent class of class-name-1.
- If the INHERITS phrase is not specified, class-name-1 forms a new root in the classification scheme. There can be one or more roots in a classification scheme.
- The WITH DATA phrase specifies that class-name-1 is able to access directly data inherited from class-name-2.