The Object-Computer paragraph provides a means of describing the computer
on which the runtime module created by the compiler is to be executed.

 It is optional.
It is optional.
 The MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT
clause are classed as obsolete elements in the ANSI'85 standard and are
scheduled to be deleted from the next full revision of the ANSI standard.
The MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT
clause are classed as obsolete elements in the ANSI'85 standard and are
scheduled to be deleted from the next full revision of the ANSI standard.
 All dialects within this COBOL implementation
support the MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT clause for documentary
purposes only. The FLAGSTD Compiler directive can be used to detect occurrences
of this syntax.
All dialects within this COBOL implementation
support the MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT clause for documentary
purposes only. The FLAGSTD Compiler directive can be used to detect occurrences
of this syntax.
 Although they are part of the standard
COBOL definition, the MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT clause are
explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not
be used in a conforming X/Open COBOL source program.
Although they are part of the standard
COBOL definition, the MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT clause are
explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not
be used in a conforming X/Open COBOL source program.
General Format
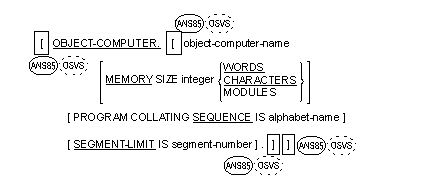
Syntax Rules
- Object-computer-name must be one user-defined COBOL word.

 The Object-Computer paragraph can
consist of only the OBJECT-COMPUTER header.
The Object-Computer paragraph can
consist of only the OBJECT-COMPUTER header.
General Rules
- The computer-name provides a means for identifying equipment
configuration. The configuration definition contains specific information
concerning the memory size. The computer-name and the MEMORY SIZE clause are
documentary only.
-
If the PROGRAM COLLATING SEQUENCE clause is not specified, the
native collating sequence is used. The appendix
Character Sets and Collating
Sequences lists both the full ASCII and EBCDIC
collating sequences. Either can be chosen as the native collating sequence by
use of the NATIVE Compiler directive.
- If the PROGRAM COLLATING SEQUENCE clause is specified, the program
collating sequence is the collating sequence associated with the alphabet-name
specified in that clause.
- The program collating sequence established in the Object-Computer
paragraph is used to determine the truth value of any nonnumeric comparisons:
- Explicitly specified in relation conditions (see the topic
Relation
Condition in the chapter Procedure
Division).
- Explicitly specified in condition-name conditions; see the topic
Condition-Name Condition
(Conditional Variable) in the chapter Procedure
Division.
- The PROGRAM COLLATING SEQUENCE clause is also applied to any nonnumeric
merge or sort keys unless the COLLATING SEQUENCE phrase of the respective SORT
or MERGE statement is specified.
- The PROGRAM COLLATING SEQUENCE clause has no effect on the ordering of
indexed files.
- The PROGRAM COLLATING SEQUENCE clause applies only to the source
element in which it is specified
 and source
elements contained within it
and source
elements contained within it
- The SEGMENT-LIMIT clause is documentary only. (See the topic
Segmentation.)
![]()
![]() It is optional.
It is optional. ![]() The MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT
clause are classed as obsolete elements in the ANSI'85 standard and are
scheduled to be deleted from the next full revision of the ANSI standard.
The MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT
clause are classed as obsolete elements in the ANSI'85 standard and are
scheduled to be deleted from the next full revision of the ANSI standard. ![]() All dialects within this COBOL implementation
support the MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT clause for documentary
purposes only. The FLAGSTD Compiler directive can be used to detect occurrences
of this syntax.
All dialects within this COBOL implementation
support the MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT clause for documentary
purposes only. The FLAGSTD Compiler directive can be used to detect occurrences
of this syntax. ![]() Although they are part of the standard
COBOL definition, the MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT clause are
explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not
be used in a conforming X/Open COBOL source program.
Although they are part of the standard
COBOL definition, the MEMORY SIZE clause and SEGMENT-LIMIT clause are
explicitly excluded from the X/Open COBOL language definitions and should not
be used in a conforming X/Open COBOL source program. 
![]() and source
elements contained within it
and source
elements contained within it